1:1 NAT allows you to map one public IP to one private IP; all traffic from that private IP to the Internet will then be mapped to the public IP specified in the 1:1 NAT mapping. This will override the Outbound NAT settings. Conversely, all traffic initiated on the Internet which is destined for the specified public IP address will then be translated to the private IP. Then it will be evaluated according to the WAN firewall ruleset, and if the traffic is permitted by the WAN rules, it will be passed to the internal node specified in the mapping.
In this scenario, the server should be accessible via the public WAN network. Thus, we will have an additional IPv4 address in each WAN network. The addresses must match the IP network and be known to the clients (e.g. via DNS).
The implementation in OPNsense is somewhat complicated because for practical purposes, the firewall requires:
- Virtual IPs
- 1:1 NAT
- Firewall rules
Virtual IPs and firewall rules have articles devoted to each settings. Assume that 192.168.2.7 is the virtual IP for the web server. To configure 1:1 NAT, do the following:
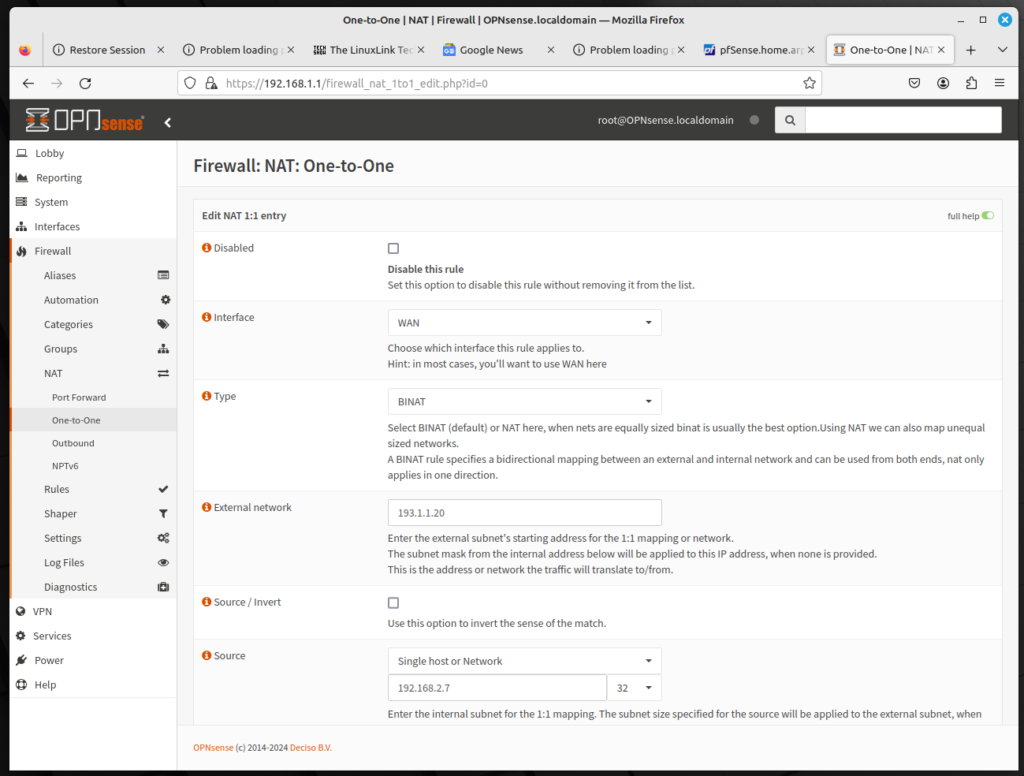
- Log into the OPNsense web GUI; on the left sidebar menu, click on Firewall, click on NAT, and click on One-to-One
- Leave Interface as WAN and for Type, leave it as BINAT. With BINAT, networks are equally sized; the NAT option allows us to map unequally sized networks
- For External network, enter the external network’s starting address.
- For Source, select Single host or Network, and type 192.168.2.7 in the edit box.
- For Description, enter a brief description (e.g. “1:1 web server”).
- For NAT reflection, leave the selection as Use system default. NAT reflection is a method that allows communication of internal PCs (behind the firerwall) to access a DMZ server using the public IP address instead of the private IP address.
- At the bottom of the page, click on Save to save the entry, then click on Apply Changes to reload the firewall rules.
You have now successfully configured 1:1 NAT for the externally-facing server.
